In today’s data-driven world, businesses and researchers are sitting on a goldmine of information. The real challenge, however, isn’t just collecting data—it’s understanding it. This is where the magic happens. We’re diving deep into the transformative world of machine learning applications in data analytics and image recognition. From predicting customer behavior to identifying diseases in medical scans, machine learning (ML) is no longer a futuristic concept; it’s a powerful tool that’s reshaping industries right now.
If you’ve ever wondered how machine learning is revolutionizing data analysis or what makes it possible for your phone to recognize your face, you’re in the right place. This comprehensive guide will walk you through everything you need to know. We’ll explore real-world examples, discuss the advanced techniques that power these innovations, and even provide a step-by-step guide on using machine learning for your own projects. Get ready to uncover how AI and machine learning are creating smarter, more efficient solutions to complex problems.
Unlocking Insights: How Machine Learning is Transforming Data Analytics
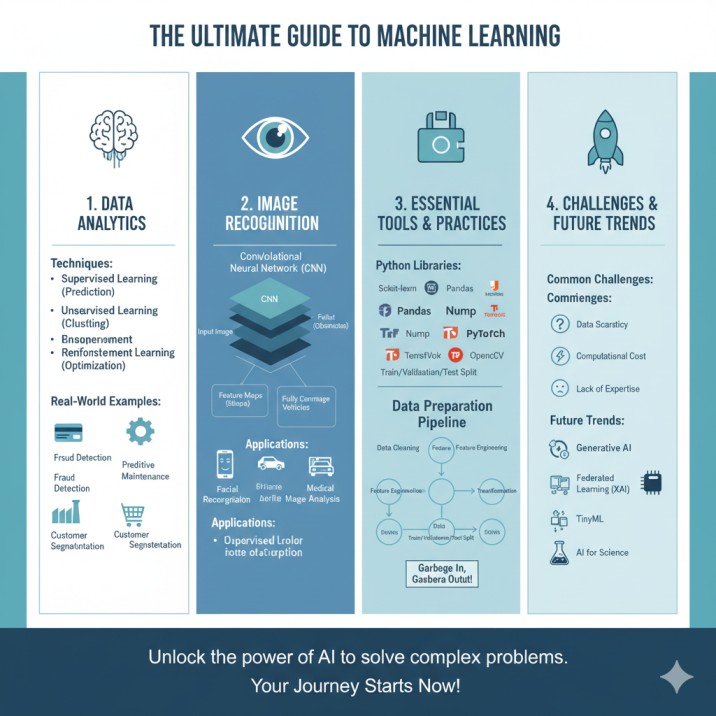
At its core, data analytics is about finding patterns and drawing conclusions from raw data. Traditionally, this involved a lot of manual work. But with machine learning, we can automate and enhance this process exponentially. ML algorithms can sift through massive datasets, identify subtle patterns humans might miss, and make incredibly accurate predictions. This synergy is unlocking unprecedented opportunities for businesses to gain a competitive edge.
What are the key machine learning techniques used in predictive data analytics?
Predictive analytics is one of the most impactful applications of machine learning in business. It uses historical data to forecast future outcomes. Imagine being able to predict which customers are likely to leave your service or which products will be in high demand next quarter. This is possible through several key ML techniques:
- Supervised Learning for Predictive Modeling: This is the most common approach. You train a model on a labeled dataset, meaning the historical data already has the correct outcomes tagged. For instance, to predict house prices, you’d use a dataset of houses with their features (size, location) and their final sale prices. Regression algorithms for forecasting sales trends are a perfect example, helping businesses with inventory management. Similarly, classification algorithms for customer churn prediction allow companies to proactively retain valuable clients.
- Unsupervised Learning for Customer Segmentation: What if your data isn’t labeled? That’s where unsupervised learning shines. It helps discover hidden structures within data. A prime example is using unsupervised learning algorithms for customer segmentation. An e-commerce company could use this to group customers based on their purchasing behavior, allowing for highly targeted marketing campaigns without any prior labels.
- Reinforcement Learning for Dynamic Optimization: This technique involves an “agent” that learns to make decisions by performing actions and receiving rewards or penalties. While more complex, it’s powerful for dynamic problems like optimizing pricing strategies in real-time or managing a supply chain.
Real-world examples of using machine learning for anomaly detection in large datasets
Anomalies are data points that deviate from the norm, and they can signify critical events like fraud, network intrusions, or equipment failure. Manually finding these needles in a digital haystack is nearly impossible.
This is a perfect job for machine learning. By learning what normal behavior looks for a system, an ML model can instantly flag any unusual activity. For example, in the financial sector, machine learning applications for fraud detection in financial transactions are a game-changer. An algorithm can analyze thousands of transactions per second, identifying patterns indicative of fraudulent activity—like a purchase in a strange location—and flagging it for review, saving companies and customers millions. Similarly, in manufacturing, ML models monitor sensor data from machinery to predict when a part might fail, enabling predictive maintenance and preventing costly downtime.
The Visual Revolution: Exploring Advanced Machine Learning Techniques for Image Recognition
Image recognition, a field within computer vision, has made astonishing leaps thanks to machine learning, particularly deep learning. This technology allows machines to “see” and interpret the visual world, a skill that has far-reaching implications across countless industries. From unlocking your smartphone with a glance to helping doctors diagnose diseases, the impact of computer vision and machine learning is profound.
The Role of Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) in Modern Computer Vision
At the heart of modern image recognition is the Convolutional Neural Network (CNN), a type of deep learning model inspired by the human visual cortex. Unlike traditional neural networks, CNNs are specifically designed to process pixel data. They use special layers called convolutional layers to automatically and adaptively learn spatial hierarchies of features from images.
Here’s a simple breakdown of how it works:
- The initial layers might learn to detect basic features like edges and corners.
- Subsequent layers combine these to recognize more complex features like shapes and textures.
- The deepest layers combine those to identify whole objects, faces, or scenes.
This hierarchical approach is what makes CNNs so powerful and is the core reason behind the recent advancements in deep learning for image recognition. For anyone interested in the technical details, the official TensorFlow documentation provides an excellent starting point for understanding and building CNNs.
A practical guide to implementing object detection models using Python
Object detection is a step beyond simple image classification (telling you what is in an image). It involves identifying where multiple objects are in an image and drawing a bounding box around each one. This is the technology that powers everything from self-driving cars identifying pedestrians to automated checkout systems recognizing products.
Building an object detection model might sound daunting, but with modern tools, it’s more accessible than ever. Here’s a simplified workflow:
- Choose a Framework: Python libraries for machine learning like TensorFlow or PyTorch are the industry standards. They come with pre-trained models like YOLO (You Only Look Once) or SSD (Single Shot MultiBox Detector) that you can fine-tune for your specific task.
- Prepare Your Data: You’ll need a dataset of images with the objects you want to detect already labeled with bounding boxes. This is often the most time-consuming part.
- Train or Fine-Tune the Model: You can load a pre-trained model and fine-tune it on your custom dataset. This process, known as transfer learning, saves a massive amount of time and computational resources.
- Evaluate and Deploy: Test your model on new images to see how well it performs. Once you’re satisfied, you can deploy it in your application.
This process is a fundamental skill for anyone looking into advanced computer vision projects using python.
Benefits of machine learning for facial recognition technology in security
Facial recognition has become a prominent application of image recognition, particularly in security. By mapping facial features from an image or video to a database, this technology can verify a person’s identity. The benefits are significant:
- Enhanced Security: It provides a seamless and secure way to control access to physical locations and digital devices.
- Law Enforcement: It helps identify suspects and find missing persons.
- Improved User Experience: It offers a frictionless method for authentication, like unlocking a phone or boarding a plane.
While there are valid ethical considerations to address, the underlying technology showcases the incredible precision of deep learning algorithms for facial feature extraction.
Industry Breakthroughs: Real-World Machine Learning Applications in Action
The theoretical power of machine learning is impressive, but its true value is demonstrated in how it solves real-world problems. Let’s explore how machine learning is being implemented in various industries, from saving lives in healthcare to creating futuristic autonomous vehicles.
How machine learning in healthcare is improving medical image analysis
The healthcare sector generates a vast amount of data, especially medical images like X-rays, MRIs, and CT scans. For radiologists, analyzing these images requires immense expertise and can be time-consuming. Machine learning is emerging as an invaluable assistant.
AI and deep learning for medical image segmentation can automatically outline organs, tumors, or other abnormalities, helping doctors with diagnosis and treatment planning. For instance, a CNN can be trained to detect signs of diabetic retinopathy from retinal scans or identify cancerous nodules in lung CT scans with a level of accuracy that can match or even exceed human experts. These benefits of using convolutional neural networks for medical image analysis are leading to earlier diagnoses and better patient outcomes.
Machine learning applications for fraud detection in the financial sector
As mentioned earlier, finance is a prime area for ML. Beyond fraud detection, machine learning is also used for:
- Algorithmic Trading: Models predict stock market movements to execute trades at optimal times.
- Credit Scoring: ML algorithms analyze thousands of data points to assess a loan applicant’s creditworthiness more accurately than traditional models.
- Customer Service: Chatbots powered by natural language processing (a branch of ML) handle customer queries 24/7.
The ability of machine learning to detect anomalies in financial data is fundamental to maintaining the integrity and security of the financial system.
The impact of image recognition on the future of autonomous vehicles
Self-driving cars are perhaps the most futuristic application of machine learning and image recognition. For a car to navigate the world safely, it must have a superhuman ability to perceive its environment. This is achieved through a suite of sensors, with cameras playing a critical role.
Image recognition models, running in real-time, perform several crucial tasks:
- Object Detection: Identifying and tracking other vehicles, pedestrians, cyclists, and traffic signs.
- Lane Detection: Ensuring the car stays within its lane.
- Semantic Segmentation: Classifying every pixel in an image to understand the road, sidewalk, sky, etc.
The development of robust machine learning models for autonomous driving is one of the most complex and challenging engineering feats of our time, and progress in this area is a testament to the power of modern AI.
Your Toolkit: Essential Tools and Best Practices for Implementation
Getting started with machine learning requires the right tools and a solid understanding of best practices. Fortunately, a vibrant open-source community has developed powerful and accessible tools, making it easier than ever to begin your journey.
What are the best Python libraries for machine learning and data science?
Python has become the de facto language for machine learning due to its simplicity and the extensive ecosystem of libraries available. If you’re looking to get started, these are the essential tools to learn:
- Scikit-learn: The perfect starting point. It offers simple and efficient tools for data mining and data analysis, with a wide range of algorithms for classification, regression, clustering, and more. It’s the focus of any good beginner’s guide to building a machine learning model with scikit-learn.
- Pandas: The ultimate tool for data manipulation and analysis. It provides data structures like DataFrames that make cleaning, transforming, and exploring data a breeze.
- NumPy: The foundational package for numerical computing in Python. It provides support for large, multi-dimensional arrays and matrices, along with a collection of mathematical functions to operate on them.
- TensorFlow and PyTorch: These are the two leading deep learning frameworks. They provide the tools to build and train complex neural networks, including CNNs for image recognition. A common question is comparing tensorflow vs pytorch, with TensorFlow often seen as better for production and scalability, while PyTorch is praised for its flexibility and ease of use in research.
- OpenCV: The go-to library for computer vision tasks. It provides tools for real-time image and video processing and integrates seamlessly with deep learning frameworks.
Best practices for preparing data for machine learning models
A common saying in the field is “garbage in, garbage out.” The performance of any machine learning model is fundamentally limited by the quality of the data it’s trained on. Addressing the issue of data quality in machine learning data analytics is arguably the most critical step in the entire process.
Here are some essential best practices:
- Data Cleaning: Handle missing values, correct inconsistencies, and remove duplicate entries.
- Feature Engineering: Create new input features from your existing data that can help the model learn better.
- Data Transformation: Scale numerical features so they are on a similar range (e.g., between 0 and 1). This prevents features with larger values from dominating the learning process.
- Splitting the Data: Divide your dataset into three parts: a training set (to train the model), a validation set (to tune the model’s parameters), and a testing set (to evaluate its final performance on unseen data). This is crucial to avoid “overfitting,” where the model memorizes the training data but fails to generalize to new data.
The Road Ahead: Overcoming Challenges and Looking to the Future
While the potential of machine learning is immense, the path to successful implementation is not without its hurdles. Understanding these challenges is key to navigating them and unlocking the full capabilities of this technology.
What are the common challenges in implementing machine learning projects?
Many organizations are eager to adopt ML, but they often run into common roadblocks:
- Data Scarcity and Quality: As discussed, high-quality labeled data is the lifeblood of supervised learning. Acquiring and preparing this data can be expensive and time-consuming.
- Computational Cost: Training large deep learning models, especially for image recognition, requires significant computational power, often involving specialized hardware like GPUs.
- Lack of Expertise: There is a high demand for skilled data scientists and machine learning engineers, and finding the right talent can be a major challenge.
- Model Interpretability: Many advanced models, like deep neural networks, act as “black boxes.” Understanding why a model made a particular decision can be difficult, which is a major concern in high-stakes fields like healthcare and finance. Research into “Explainable AI” (XAI) is an active area aimed at solving this very problem. For an overview, you might refer to foundational papers available on resources like arXiv.org.
The future of machine learning: trends in data analytics and image recognition
The field of machine learning is evolving at a breathtaking pace. Looking ahead, several exciting trends are set to define the next era of AI:
- Generative AI: Models like GPT-4 and DALL-E 2 have shown an incredible ability to generate new text, images, and code. This will continue to transform creative industries and data augmentation processes.
- Federated Learning: This approach allows models to be trained across multiple decentralized devices (like mobile phones) without the data ever leaving the device, addressing critical privacy concerns.
- TinyML: This involves running machine learning models on low-power microcontrollers, enabling smart, connected devices on the edge without needing to send data to the cloud.
- AI for Science: ML is accelerating scientific discovery in fields like drug discovery, materials science, and climate modeling by analyzing complex experimental data at an unprecedented scale.
The future trends in machine learning for autonomous systems and data analysis point towards more automated, more efficient, and more intelligent systems that will be seamlessly integrated into our daily lives.
Conclusion: Your Journey into Machine Learning Starts Now
We’ve traveled from the foundational concepts of machine learning in data analytics to the cutting-edge applications of deep learning in image recognition. It’s clear that these technologies are not just changing the game—they’re creating a whole new one. By enabling us to make smarter predictions, uncover hidden patterns, and interpret the visual world, machine learning is empowering us to solve problems that were once considered impossible.
Whether you’re a business leader looking to leverage your data, a developer eager to build intelligent applications, or simply a curious mind fascinated by the future of technology, the journey into machine learning is one of the most rewarding you can take. The tools are accessible, the community is supportive, and the potential for innovation is limitless.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. What is the main difference between machine learning and traditional data analysis?
Traditional data analysis often relies on static models and human-guided exploration to find insights. Machine learning, on the other hand, involves building models that can learn and adapt from data automatically to make predictions or decisions without being explicitly programmed for each task.
2. How can a small business start using machine learning for data analytics?
A great starting point is to use cloud-based ML platforms like Google AI Platform or Amazon SageMaker, which offer user-friendly tools. Start with a clear business problem, like predicting customer churn, and use a clean dataset. Even simple models built with scikit-learn can provide valuable insights.
3. Is learning to code necessary to work with machine learning?
While coding (especially Python) is essential for developing custom models, there are many low-code or no-code ML platforms available today that allow users to build and deploy models using a graphical interface, making it more accessible to non-programmers.
4. What are some ethical considerations in using machine learning for image recognition?
Key ethical issues include privacy concerns with facial recognition surveillance, the potential for bias in algorithms (e.g., performing worse on certain demographics), and the security of biometric data. It’s crucial to develop and deploy these technologies responsibly.
5. How does machine learning handle big data processing?
Machine learning is ideal for big data because its algorithms are designed to scale and find patterns in massive, complex datasets. Frameworks like Apache Spark are specifically built to distribute the computational workload across multiple machines, making it possible to train models on petabytes of data.
6. What is transfer learning and why is it important for image recognition?
Transfer learning is a technique where a model developed for one task is repurposed as the starting point for a model on a second task. In image recognition, you can use a powerful model pre-trained on a huge dataset (like ImageNet) and fine-tune it on your smaller, specific dataset. This saves enormous amounts of time and data.
7. Can machine learning predict stock market prices accurately?
While many use machine learning for algorithmic trading, predicting the stock market with high accuracy is extremely difficult due to its complexity and the amount of random, unpredictable events (“noise”). ML can identify trends and patterns but cannot predict the future with certainty.
8. What is the difference between supervised and unsupervised learning in a practical sense?
In a practical sense, you use supervised learning when you have a specific target you want to predict (e.g., sales, fraud, disease) and historical data where the answer is known. You use unsupervised learning when you want to explore the data to find inherent groupings or patterns without a predefined outcome (e.g., finding customer segments).
9. What are the best open-source datasets for practicing image recognition?
Some popular choices include ImageNet (a massive dataset for object recognition), COCO (Common Objects in Context), MNIST (for handwritten digit recognition, great for beginners), and CIFAR-10/100 (for more complex object recognition).
10. How long does it take to train a complex deep learning model?
This can vary wildly, from a few minutes to several weeks. It depends on the size of the model, the amount of data, and the available hardware. Training a state-of-the-art image recognition model from scratch on a large dataset often requires multiple high-end GPUs running for days.
11. What is the relationship between AI, Machine Learning, and Deep Learning?
Think of them as nested concepts. Artificial Intelligence (AI) is the broad field of creating intelligent machines. Machine Learning (ML) is a subfield of AI that focuses on giving machines the ability to learn from data. Deep Learning is a subfield of ML that uses complex, multi-layered neural networks to solve problems, and it’s particularly dominant in image and speech recognition.
12. What are the first steps for someone wanting to learn machine learning?
Start with the fundamentals of Python, then learn key libraries like NumPy, Pandas, and Scikit-learn. Take an introductory online course to understand the core concepts of different algorithms. Finally, work on hands-on projects with real datasets to build practical experience. This practical application is key to solidifying your knowledge.