Welcome to 2026. The digital world is no longer just a place we visit; it’s where we live, work, and operate. But this interconnectedness has created a complex and dangerous new frontier. The cyber threats of today are not the simple viruses of the past. We are now facing AI-driven attacks that think, adaptive ransomware that extorts, and vulnerabilities in every smart device we own.
Sticking your head in the sand is not an option. Whether you’re a small business owner, an IT manager, or a concerned remote worker, understanding the emerging cybersecurity threats for 2026 is the first step to building a digital fortress.
This guide will be your partner in that mission. We’ll break down the most significant dangers you face in simple, human terms. More importantly, we’ll give you actionable cybersecurity defense strategies for businesses and individuals. We will cover the evolution of ransomware attacks, explore how AI-driven cyber attacks are changing the game, and introduce the powerful defensive tools—like Zero Trust architecture and business VPNs—that will keep you safe.
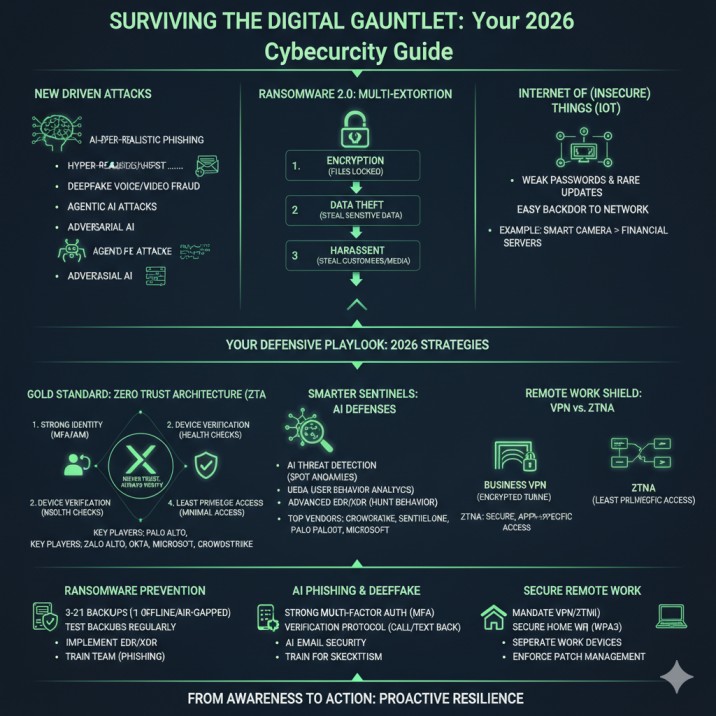
The New Wave of Threats: What’s Coming in 2026
The threat landscape has evolved. It’s faster, smarter, and more ruthless. Here are the primary dangers on your radar for 2026.
The Rise of the Machines: AI-Driven Cyber Attacks
This is the number one game-changer. Hackers are now using the same artificial intelligence tools that we use to write emails and create art. But they’re using them for a new generation of advanced persistent threats (APTs).
- Generative AI for Hyper-Realistic Phishing: Forget the old emails with bad grammar and “Dear Sir/Madam.” In 2026, attackers use Generative AI to craft perfect, personalized phishing emails. These messages can reference recent projects, mimic your CEO’s exact writing style, or even mention a real meeting you had yesterday. They are almost impossible to distinguish from legitimate communication.
- AI-Powered Deepfakes for Voice & Video Fraud: This is the stuff of nightmares. An attacker can use AI to clone your CFO’s voice. You then get a call, and it sounds exactly like them, creating a sense of urgency: “I’m in a bind, I need you to wire $50,000 to this new vendor immediately. I can’t talk, just get it done.” This deepfake voice scam for financial fraud is incredibly effective.
- “Agentic AI” Attacks: This is the next frontier. These are autonomous AI “agents” that hackers can release. These agents are tasked with a simple goal: “breach this company.” The AI will then probe your network, discover vulnerabilities, craft custom malware, and steal your data all on its own, 24/7, without a human operator. It’s like a robotic burglar that never sleeps.
- Adversarial AI: This is a more subtle attack. Instead of attacking you directly, hackers use AI to “poison” the data that your defensive AI tools learn from. This can slowly teach your security system that a malicious file is “safe,” creating a blind spot that attackers can exploit later.
Ransomware 2.0: It’s Not Just About Encryption Anymore
Ransomware is still a massive threat, but the business model has changed. The evolution of ransomware attacks has led to a strategy called “double and triple extortion.”
- Stage 1: Encryption (The Old Way): The attacker encrypts all your files and demands a ransom to unlock them.
- Stage 2: Data Theft (Double Extortion): Before they encrypt, they steal a copy of all your most sensitive data—customer lists, employee records, financial reports, intellectual property. Now, they threaten to publicly leak this data if you don’t pay. This is a PR and legal disaster.
- Stage 3: Harassment (Triple Extortion): If you still refuse to pay, the attackers go a step further. They will contact your customers, clients, partners, and even the media directly. They might email your customers, “Your private data was stolen from [Your Company]. Tell them to pay, or we will release it.” They effectively turn your own network against you.
This multi-layered ransomware extortion tactic makes recovery much harder. Even if you have backups, you still have to deal with the data theft and public fallout.
The Internet of (Insecure) Things: IoT Security Risks
Every smart device is a computer. Your office smart thermostat, the security cameras, the smart printer, and even the “smart” coffee machine are all connected to your network. Unfortunately, IoT security best practices for 2026 are still lagging.
These devices are often shipped with weak, default passwords (like “admin”) and are rarely updated. For a hacker, that smart camera is a wide-open, undefended back door into your entire corporate network. They won’t hack the camera to spy on you; they’ll hack it to pivot and gain access to your financial servers.
Your 2026 Defensive Playbook: Tools & Strategies That Work
The threats are scary, but they are not unbeatable. A modern defense is about layers, intelligence, and a new way of thinking. You can no longer build a “castle wall” and assume you’re safe. You must assume the attacker is already inside.
The Gold Standard: Implementing a Zero Trust Architecture (ZTA)
This is the single most important strategic shift your business can make. The old model was “trust but verify”—if you were inside the office network, you were trusted.
The Zero Trust security model is simple: “Never trust, always verify.”
It assumes that every user and every device could be compromised. No one gets access to anything until they are positively identified and authorized for that specific resource, at that specific moment.
[Image of a Zero Trust Architecture diagram]
A practical guide to implementing Zero Trust involves several key pillars:
- Strong Identity: You must know who is asking for access. This is where Identity and Access Management (IAM) solutions come in.
- Device Verification: You must know the device is safe. Is it a known company laptop? Is its antivirus up to date?
- Micro-segmentation: You break your network into tiny, isolated zones. Even if an attacker breaches one “zone” (like a single laptop), they are trapped. They can’t move laterally to your data servers.
- Least Privilege Access: Every user and application only gets the absolute minimum level of access they need to do their job. Your marketing intern does not need access to the payroll database.
You don’t have to build this from scratch. Many top cybersecurity companies in Zero Trust offer comprehensive solutions. Key players in this space include:
- Zscaler: A cloud-native leader that secures access to apps.
- Palo Alto Networks: A giant in network security with a strong Zero Trust platform.
- Okta: A market leader in Identity and Access Management (IAM), a core piece of ZTA.
- Microsoft (Entra ID): Deeply integrated into the Azure and Windows ecosystem.
- CrowdStrike: Extends Zero Trust principles to the endpoint (your devices).
Smarter Sentinels: AI-Driven Cybersecurity Defenses
The only way to fight AI-driven attacks is with AI-driven defenses. Your human security team can’t watch every log file 24/7, but an AI can.
- AI in Threat Detection: Modern tools use machine learning to build a “baseline” of your network’s normal behavior. When it detects an anomaly—like a user suddenly accessing a server they’ve never touched before at 3 AM—it flags it instantly.
- User and Entity Behavior Analytics (UEBA): This is a key part of AI in cybersecurity. It specifically monitors user accounts for signs of compromise, such as logging in from two different countries at once or suddenly trying to download massive amounts of data.
- Advanced EDR and XDR: Your old antivirus is obsolete. You now need Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) or Extended Detection and Response (XDR). These tools, powered by AI, don’t just look for known viruses. They hunt for suspicious behavior.
- Top EDR/XDR Vendors for 2026:
- CrowdStrike (Falcon): A cloud-native, AI-powered industry leader.
- SentinelOne (Singularity): Known for its powerful autonomous AI response.
- Palo Alto Networks (Cortex XDR): Integrates network, endpoint, and cloud data.
- Microsoft Defender for Endpoint: A strong contender, especially for those invested in the Microsoft ecosystem.
- Top EDR/XDR Vendors for 2026:
The Remote Work Shield: Business VPNs vs. ZTNA
With remote work as the new normal, the cybersecurity challenges of a remote workforce are huge. How do you secure an employee working from a coffee shop?
- The Traditional Tool: Business VPNs: A Virtual Private Network (VPN) creates an encrypted “tunnel” from your employee’s laptop back to the company network. This is a good first step. It encrypts their traffic and hides it from anyone on the public Wi-Fi.
- Best VPNs for Business in 2026:
- NordLayer (from NordVPN): Built specifically for business with a focus on ease of use and security.
- Surfshark: Offers business plans with dedicated IPs and team management.
- Proton VPN for Business: Comes from a company with a massive reputation in privacy and security.
- Best VPNs for Business in 2026:
- The Better Tool: Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA): A VPN has a flaw: it’s all-or-nothing. Once you’re “in” the tunnel, you’re on the company network, which can violate Zero Trust principles. ZTNA (a core part of ZTA) is the upgrade. It gives users a secure tunnel only to the specific application they need, and nothing else. They never get full network access.
Your Practical Prevention Checklists for 2026
All this strategy is great, but what can you do right now? Here are actionable checklists.
Ransomware Prevention Checklist (2026 Edition)
- Backups (The 3-2-1 Rule): Keep 3 copies of your data, on 2 different types of media (e.t., a local disk and the cloud), with 1 copy kept offline and “air-gapped.” An air-gapped backup is not connected to any network, so ransomware can’t touch it.
- Test Your Backups: A backup you haven’t tested is not a backup. Regularly try to restore a file to ensure it works.
- Implement EDR/XDR: Use tools like CrowdStrike or SentinelOne to detect ransomware behavior before it can encrypt.
- Patch Everything, Immediately: Apply security updates for your operating systems and software as soon as they are released.
- Train Your Team: The #1 entry point for ransomware is a phishing email. Train your staff to recognize and report suspicious emails.
- Invest in Recovery Solutions: Look into services like Druva or Nasuni that offer immutable (unchangeable) backups and rapid recovery features specifically for ransomware.
AI-Driven Phishing & Deepfake Prevention Checklist
- Use Strong Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): This is your best defense. Even if an attacker steals a password, they can’t log in without the second factor (a code from your phone app). Use app-based authenticators, not just SMS.
- Establish a “Verification” Protocol: Create a company policy for any sensitive request (like wiring money or changing credentials). This request must be verified through a different communication channel.
- Example: If you get an urgent email from your boss, you must confirm it with a text or a call to their known number. If you get a voice call, you must call them back on their trusted number.
- AI-Powered Email Security: Your basic email filter isn’t enough. You need advanced tools that use AI to analyze the intent and language of an email to spot sophisticated phishing.
- Train for Skepticism: Teach your employees to be on high alert for any message that uses urgency, fear, or authority to rush them into an action.
Securing Your Remote Workforce Checklist
- Mandate a Business VPN or ZTNA: No employee connects to any company resource without using the company-provided secure connection.
- Secure Home Wi-Fi: Ensure all employees change the default password on their home routers and use strong WPA3 encryption.
- Separate Work and Personal Devices: If possible, provide company-owned laptops. If you must use a Bring Your Own Device (BYOD) policy, use EDR and ZTNA tools to create a secure, isolated container for work on that personal device.
- Enforce Patch Management: Use a tool to ensure all remote devices (even personal ones accessing company data) have the latest security updates.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) About 2026 Cybersecurity
1. What is the single biggest cybersecurity threat for 2026?
AI-driven cyber attacks. Their ability to automate, personalize, and scale attacks (like deepfake fraud and hyper-realistic phishing) represents the biggest shift in the threat landscape.
2. Is a VPN enough to keep my business safe in 2026?
No. A VPN is a good tool, especially for remote work, but it’s not a complete strategy. It’s one piece of a much larger puzzle. It should be combined with a Zero Trust architecture, EDR, and strong Identity and Access Management (IAM).
3. What is the difference between EDR and XDR?
EDR (Endpoint Detection and Response) focuses on your “endpoints”—devices like laptops and servers. XDR (Extended Detection and Response) is the evolution. It collects and correlates threat data from multiple sources, including endpoints, your network, cloud applications, and email, to give you a single, unified view of a threat.
4. We’re a small business. Isn’t a Zero Trust model too complex for us?
Not anymore. It used to be, but now many vendors like Zscaler, Okta, and NordLayer offer “as-a-service” solutions that are designed to be affordable and easy to implement, even for small teams without a dedicated IT staff.
5. How do I actually start implementing Zero Trust?
Start with identity. The first and most crucial step is ensuring every user has a unique, secured identity. Implementing a strong IAM solution (like Okta, CyberArk, or Microsoft Entra ID) and enforcing Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) for everyone is the best first step.
6. What is a “supply chain attack”?
This is a major threat. Instead of attacking you, hackers attack one of your less secure vendors or software suppliers. They insert malicious code into a software update that you trust. When you download the “safe” update, you’ve just invited the attacker in. A Zero Trust model helps defend against this.
7. Can’t AI-driven defenses be beaten by AI-driven attacks?
This is the new “arms race.” Yes, attackers will use AI to try and fool defensive AI. This is why it’s crucial to partner with top-tier vendors (like those mentioned) who are investing heavily in adversarial AI research to keep their defensive models one step ahead.
8. What is the “human firewall” I keep hearing about?
Your people are your last line of defense. A human firewall refers to a well-trained, security-conscious workforce. When your technology fails to stop a sophisticated phishing email, a trained employee who knows to report the email instead of clicking it becomes your most valuable security asset. Regular security awareness training is how you build it.
9. How does quantum computing affect cybersecurity in 2026?
In 2026, quantum computing is not an immediate threat, but it’s a looming one. A powerful-enough quantum computer will one day be able to break most of the encryption we use today. The good news is that we are still years away from that. The real work in 2026 is for organizations to start post-quantum cryptography (PQC) planning and inventorying their data so they are ready to upgrade.
10. What is an “air-gapped” backup?
An air-gapped backup is one that is physically disconnected from any network. This could be an external hard drive that you unplug and store in a safe, or a backup on a tape. Because it’s not connected, ransomware cannot find or encrypt it, making it your ultimate insurance policy.
11. Is my IoT smart-light bulb really a security risk?
Yes. A hacker can exploit a vulnerability in that light bulb, get onto your Wi-Fi network, and then “move laterally” to find your laptop or file server. The best practice for IoT security is to put all your “smart” devices on a separate, isolated “Guest” Wi-Fi network. This way, even if a device is hacked, it can’t access your important computers.
12. What are the top ransomware recovery solutions?
Look for solutions that offer “immutable snapshots” (backups that can’t be changed or deleted by ransomware) and fast recovery. Top players in this space include Druva, Cohesity, Rubrik, and Nasuni.
Your Next Move: From Awareness to Action
The cybersecurity landscape of 2026 is undeniably complex. But it is not hopeless. The guiding principle for this new era is proactive resilience.
Don’t wait for a breach to happen. Start today. Review your defenses. Have an honest conversation about your risks. Move one step closer to a Zero Trust model, even if it’s just enforcing MFA for all employees. Train your people. And test your backups.
The future of your business may depend on it.