Let’s be honest. The traditional “Know Your Customer” (KYC) process in banking is broken.
For customers, it’s a nightmare of friction. Finding physical documents, scanning them, waiting days, or even visiting a branch—it’s no wonder customer onboarding abandonment rates are sky-high. For financial institutions, it’s a costly, leaky bucket. You spend millions on manual verification, compliance teams, and fraud prevention, yet financial crime, advanced identity fraud techniques, and regulatory fines are all on the rise.
The game has changed. We’re no longer just fighting simple fraud; we’re fighting preventing synthetic identity fraud in banking, battling sophisticated deepfakes, and trying to secure a borderless, digital-first financial world.
The old stack of manual checks and siloed databases can’t keep up.
What financial platforms need is a new foundation. Not just a single tool, but an entirely new tech stack. That new stack is Digital Identity as a Service (IDaaS). This isn’t just an upgrade; it’s a revolution in how we establish trust online. It’s the key to delivering the seamless and secure KYC that both customers and regulators demand.
Why Traditional KYC Workflows are Failing Financial Institutions
Before we build the new house, we need to understand why the old one is collapsing. The traditional KYC model was built for a physical, paper-based world, and it’s failing spectacularly in the digital age.
The Skyrocketing Cost of Manual KYC Verification
The cost of manual KYC verification is a drain on resources. This process relies on teams of people to manually review passports, driver’s licenses, and utility bills. This is not only slow but also incredibly expensive.
Every human touchpoint introduces potential for:
- High Operational Costs: You are paying for labor, not automation. The KYC compliance costs continue to rise as regulations get tighter.
- Human Error: A tired analyst might miss a subtle forgery or a data entry error, leading to non-compliance or, worse, letting a fraudster slip through.
- Inefficient KYC Processes: The workflow is linear and slow. A customer submits documents and then… waits. This “wait” is where you lose business.
The Customer Experience Nightmare: High Friction, High Drop-Off
Today’s customers expect a digital-first, instant experience. If they can open a social media account in 30 seconds, why does it take three days to open a bank account? This is the core of poor customer experience in banking.
When a customer hits a wall of friction—like being asked to upload a document for the third time—they don’t call support. They just leave. This is the customer onboarding abandonment that kills growth for fintechs and digital banks. The challenge is figuring out how to reduce KYC friction for customers without compromising security.
The Evolving Threat Landscape: A Playground for Fraudsters
The most significant failure of traditional KYC is its inability to stop modern fraud. Fraudsters are using AI and sophisticated tools to create identities from scratch.
- Synthetic Identity Fraud: This is where a criminal combines real (but stolen) and fake information—like a real Social Security number with a fake name and address—to create a “new” person. This identity builds a credit history and then “busts out,” disappearing with thousands of dollars.
- Deepfakes: We’re no longer talking about bad Photoshop. Deepfake detection for KYC is now a critical need. Fraudsters can use AI to create realistic videos or images that pass simple liveness checks, fooling human reviewers and basic systems.
- Account Takeover: Weak authentication (like simple passwords) makes it easy for criminals to take over existing accounts, bypassing KYC entirely.
Traditional methods that just check a document against a database are blind to these advanced identity fraud techniques.
What is Digital Identity as a Service (IDaaS) and How Does it Work?
This is where Digital Identity as a Service (IDaaS) enters the picture. It’s a fundamental shift in thinking.
Beyond Just a Tool: IDaaS as a Cloud-Based IAM Solution
What is Digital Identity as a Service? At its core, IDaaS is a cloud-based subscription service that manages identity and access management (IAM) for you. Instead of building and maintaining your own complex, expensive, and high-maintenance identity-checking systems, you plug into an expert provider via an API.
This provider handles all the heavy lifting: the document verification, the biometric scanning, the fraud checks, the compliance updates. This is the cloud-based identity verification platform model.
The Core Benefits of IDaaS for Financial Institutions
Adopting an IDaaS model isn’t just about outsourcing; it’s about upgrading your entire operation.
- Massive Cost Reduction: You are automating KYC workflows with IDaaS, which means you can stop paying for repetitive manual labor and focus your expert teams on high-risk cases. This directly reduces operational costs with digital KYC.
- Unprecedented Scalability: A scalable KYC solution is essential for growth. Whether you are a fintech onboarding 10,000 new users in a day or a global bank entering a new market, a cloud-based IDaaS platform scales with you instantly.
- Drastically Faster Onboarding: What took days now takes minutes, or even seconds. This creates the seamless customer onboarding for financial services that wins and retains customers.
- Superior Security and Compliance: IDaaS providers are specialists. Their entire business model depends on being ahead of fraudsters and on top of regulations. They employ security technologies like phishing-resistant passwordless authentication and adaptive security that you simply couldn’t build in-house cost-effectively.
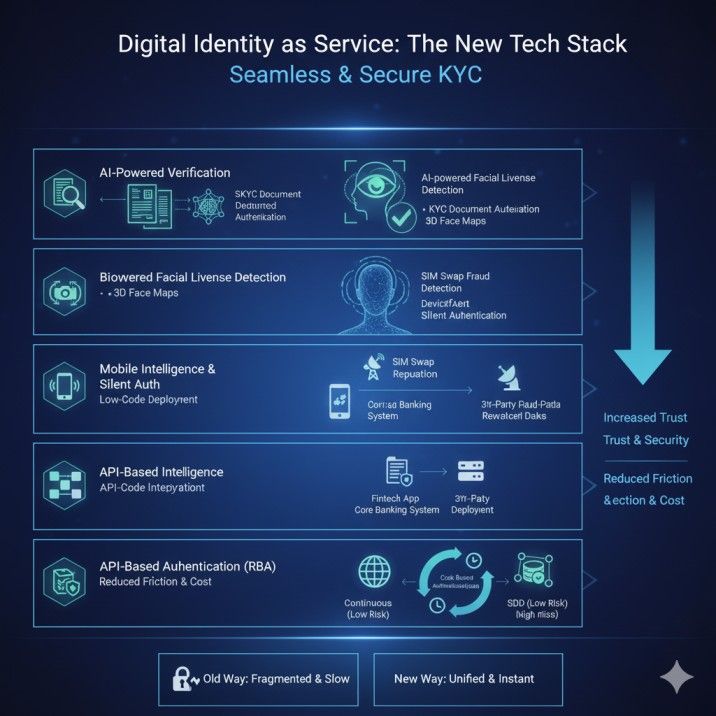
The Shift to a User-Centric Digital Identity Model
The most profound change IDaaS enables is the move toward a user-centric digital identity model.
The old way: Every bank, every app, every service forces you to re-verify your identity from scratch. It’s inefficient and leaves your personal data scattered in dozens of databases, just waiting to be breached.
The new way: A reusable KYC identity. A customer verifies their identity once with a trusted IDaaS provider. This verification is then stored in a secure digital wallet on their phone, which they control. When they want to open an account with a new bank, they simply grant that bank permission to access their pre-verified credentials.
This is the concept behind Self-Sovereign Identity (SSI). The user owns and controls their identity, and financial institutions get to consume a trusted, verified, and secure credential instantly. This is the ultimate “seamless” experience.
Deconstructing the Modern Digital Identity Tech Stack
So, what is actually in this new tech stack? “IDaaS” is the service model, but it’s powered by a layered stack of advanced technologies. Let’s break it down.
Layer 1: AI-Powered Identity Proofing and Verification
This is the front door. When a user holds up their driver’s license to their phone camera, this layer gets to work.
- Automated Document Verification: This isn’t just a photo. The system uses Optical Character Recognition (OCR) for KYC to instantly read the text.
- KYC Document Authentication: AI scans for holographic overlays, microprint, and other security features to ensure the document is legitimate and not a forgery. It checks for font inconsistencies, pixel-level anomalies, and other signs of digital tampering.
Layer 2: The Power of Biometrics and Liveness Detection
This layer answers the critical question: “Is the person holding the ID the real person, and are they live?”
This is where we defeat deepfakes. AI-powered facial liveness detection is crucial.
- Active vs. Passive Liveness: Basic systems (active) ask you to “blink” or “turn your head.” Advanced systems use passive biometric authentication. They analyze the user’s video feed for biological indicators of liveness—like subtle skin texture changes, eye movements, and lighting reflections—that a 2D photo or even a deepfake video can’t replicate.
- 3D Face Maps: The system creates a 3D face map for identity verification, comparing the geometry of the user’s face to the photo on their ID with incredible accuracy. This combination of voice and face liveness detection provides an extremely high-assurance check.
Layer 3: Silent Authentication and Mobile Intelligence
This is one of the most advanced and “seamless” layers. Many users won’t even know it’s happening, which is the point.
What is mobile number intelligence? The system uses your phone number as a key data point for trust. It can silently check:
- SIM Swap Fraud: Has this phone number been “ported” to a new SIM card in the last 24 hours? This is a massive red flag for account takeover. The system can detect SIM swap fraud and trigger a “step-up” challenge.
- Device Reputation: Is this device associated with a known fraud network?
- Silent Authentication: For logging in, the system can use silent authentication for secure login, verifying the user’s identity through their mobile network’s secure connection without even needing a password or an SMS code.
Layer 4: API-Based Integration for a Seamless Ecosystem
This new stack is useless if it’s a silo. The “glue” that holds it all together is the Application Programming Interface (API).
An API-based identity verification for fintech apps is what allows a new digital bank to have a world-class KYC system up and running in days, not years.
- Low-Code Deployment: Many IDaaS platforms offer a no-code KYC platform or low-code deployment for KYC. This means your developers don’t have to write complex code; they just drag and drop verification steps into their existing app’s workflow.
- Core Banking Integration: This allows for integrating IDaaS with core banking systems. The moment a user is verified, their account can be provisioned, and their risk profile is automatically set in the central system.
Layer 5: Continuous Monitoring and Risk-Based Authentication (RBA)
KYC isn’t “one and done.” Trust is not static; it’s continuous. This is perhaps the most critical failure of traditional systems.
- Continuous Monitoring and Risk Intelligence: The IDaaS platform continuously screens verified customers against global watchlists, sanctions lists, and politically exposed persons (PEP) lists.
- Adaptive Risk-Based Authentication (RBA): This is the future of security. Instead of treating every login the same, the system assesses the risk in real-time.
- Logging in from your usual device and location? No password needed.
- Trying to wire $50,000 from a new device in a different country? The system will “step up” the authentication, triggering a real-time identity verification with a face scan.
- Event-Driven KYC Reviews: Instead of annoying your low-risk clients with a “periodic review” every year, the system triggers a review only when a high-risk event occurs, like a massive transaction or a hit on a sanctions list.
Navigating the Complex Web of KYC and AML Compliance
This new tech stack isn’t just for a better customer experience. It’s a powerful tool for navigating the crushing complexity of financial compliance.
Meeting Global Standards: FATF, AML, and CTF
Regulators are no longer optional. The Financial Action Task Force (FATF), the global anti-money laundering (AML) and counter-terrorist financing (CTF) watchdog, sets the standards.
When the FATF places a country on its “grey list” (for FATF strategic deficiencies), it signals to the world that its financial system has a high risk. Financial institutions operating there face intense scrutiny. An advanced IDaaS platform is the best way to demonstrate a robust, auditable, and effective compliance program. It shows you are taking a proactive, risk-based approach to AML.
You can learn more about these global standards directly from the Financial Action Task Force (FATF).
The Risk-Based Approach: From CDD to EDD
Compliance isn’t one-size-fits-all. The “risk-based approach” is the core principle.
- Simplified Due Diligence (SDD): For low-risk clients (e.g., opening a simple savings account), the verification can be fast and light.
- Customer Due Diligence (CDD): This is the standard level of verification for most customers.
- Enhanced Due Diligence (EDD): This is a much deeper investigation triggered for high-risk clients. When to apply Enhanced Due Diligence (EDD) is a critical decision. This could be for a Politically Exposed Person (PEP) or a high-net-worth individual involved in complex offshore structures.
A modern IDaaS stack automates this. It assesses the risk score during onboarding and automatically routes the customer to the correct SDD, CDD, or EDD workflow. This is a key part of KYC lifecycle management.
Data Privacy and Governance: Embedding Trust
In a world of data breaches and GDPR, you can’t be careless with customer identity. A major benefit of IDaaS is superior data governance.
- Privacy-Safe Data Retention: The IDaaS provider manages the secure “vault” for the identity data, ensuring it’s encrypted and stored in compliance with laws like GDPR.
- Privacy-First Local Biometric Storage: Advanced systems practice this. Your 3D face map isn’t stored on a bank’s server; it’s stored as a cryptographic hash on your own phone. The bank never “sees” your face; it just gets a “yes” or “no” answer from the cryptographic check.
- Explainable AI: When a regulator asks why your AI-based system declined a customer, you need an answer. Explainable AI in KYC decisions provides a clear audit trail, showing which rules and risk factors led to a specific decision, ensuring transparency and fairness.
What’s Next? The Future of Digital Identity in Banking
This new tech stack is the foundation, but the building is still going up. The future of digital identity in banking is even more integrated and intelligent.
The Rise of Decentralized Identity and Verifiable Credentials
This is the full realization of the “user-centric” model. We are moving towards Decentralized Identity (DID), often secured by blockchain for digital identity.
In this model, your identity (your “driver’s license,” “university degree,” “bank account verification”) exists as a verifiable credential. You hold these credentials in your secure digital wallet. When a platform needs to know your age, you don’t show them your whole driver’s license (with your address and license number); you just share the “verifiable credential” that proves you are over 21. This is the ultimate in privacy and user control.
Agentic AI and the Proactive KYC Agent
The next step beyond simple automation is Agentic AI. Think of what is Agentic AI in KYC as a team of autonomous AI “agents” working for your compliance department.
One AI agent’s entire job is proactive fraud detection, scanning millions of transactions for new, unseen patterns. Another’s job is compliance monitoring, reading new regulatory documents from the European Banking Authority and suggesting changes to your KYC workflows before you’re non-compliant.
One Identity, All Platforms: The Push for Interoperability
The final goal is a single digital identity for all financial services. This is the push for a global digital identity network.
Imagine a world where your single, secure, verified digital identity allows you to open a bank account in London, invest in a stock in New-York, and get a loan in Singapore—all in a matter of seconds. This will require solving massive cross-border KYC compliance challenges, but it is the ultimate vision for a truly seamless and secure global financial ecosystem.
Conclusion: Adopt the New Stack or Be Left Behind
The days of slow, costly, and high-friction KYC are over. They have to be. The demands of customers for a seamless experience and the threats from sophisticated fraudsters have made the old model obsolete.
Digital Identity as a Service (IDaaS) is not just another vendor product. It is the new, integrated technology stack that provides the answer. It combines AI-powered verification, biometric liveness, mobile intelligence, and continuous risk monitoring into a single, scalable, API-driven service.
For financial institutions, this is the moment to stop patching the old, broken system. It’s time to build on a new foundation. Adopting the new digital identity tech stack is no longer a competitive advantage; it’s a survival requirement for future-proofing financial services and, most importantly, for building customer trust with secure KYC in a digital-first world.
Frequently Asked Questions About Digital Identity as a Service and KYC
1. What is the main difference between KYC (Know Your Customer) and AML (Anti-Money Laundering)?
- KYC is the process of verifying a customer’s identity to ensure they are who they say they are. It’s the “Know Your Customer” part. AML is the broader strategy and set of laws to prevent the financial system from being used for illegal activities. KYC is a foundational part of a strong AML program.
2. Is digital KYC more secure than traditional manual KYC?
- Yes, significantly. Manual KYC is vulnerable to human error and high-quality forged documents. Advanced digital KYC solutions use AI, biometrics, and liveness detection to spot deepfakes and document fraud that a human would miss. Combined with continuous monitoring, it’s a far more robust system.
3. How long does a modern digital KYC check take?
- While it can vary based on the risk level, many modern real-time identity verification processes can be completed in under 60 seconds. This is a massive improvement from the days or weeks of manual verification.
4. What is a “risk-based approach” in KYC?
- It means you don’t treat all customers the same. You apply different levels of verification based on their risk profile. A low-risk customer might go through a Simplified Due Diligence (SDD) process, while a high-risk customer (like a Politically Exposed Person) will automatically trigger an Enhanced Due Diligence (EDD) workflow.
5. What is synthetic identity fraud, and how does IDaaS help prevent it?
- Synthetic identity fraud is when a criminal creates a new identity by combining real and fake information (e.g., a stolen Social Security number with a fake name). Traditional KYC (which just checks if a document is “real”) can miss this. A modern IDaaS stack cross-references data from multiple sources, uses AI-powered identity proofing, and looks for behavioral red flags to detect these “ghost” identities.
6. What is a “reusable identity” or “reusable KYC”?
- This is a user-centric concept where a customer verifies their identity once with a trusted provider. They can then reuse this digital “proof” to instantly open accounts at other banks or services that trust that provider, without having to upload their passport and personal details every single time.
7. How does “liveness detection” work, and why is it important?
- Liveness detection ensures the person providing the biometric (like a face) is a real, live human—not a photo, a mask, or a deepfake video. AI-powered facial liveness detection analyzes subtle cues like blinking, skin texture, and light reflections to prove “presence.” It’s critical for stopping simple spoofing attacks.
8. What is the role of APIs in digital KYC?
- APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) are the “messengers” that allow different software systems to talk to each other. An API-based identity verification service allows a fintech app to “call” the IDaaS provider’s service to run a KYC check and get a “yes” or “no” result back instantly, all without having to build the complex verification technology themselves.
9. What are the biggest challenges in implementing a digital KYC system?
- The top challenges are often integrating IDaaS with core banking systems (which can be old), managing data privacy regulations across different countries (cross-border KYC compliance), and ensuring the user experience is truly simple and doesn’t just replace one type of friction with another.
10. What is “step-up authentication”?
- This is an intelligent security feature of a risk-based authentication (RBA) system. Instead of always asking for a high level of security, it “steps up” the challenge based on risk. A low-risk login might be seamless, but a high-risk transaction (like wiring money) will trigger a “step-up” to a more secure check, like a face scan.
11. Can digital KYC solutions use blockchain?
- Yes. Blockchain for digital identity is a key technology for enabling Decentralized Identity (DID) and Self-Sovereign Identity (SSI). It can be used to create a tamper-proof, auditable record of verification that the user controls, rather than a bank or government.
12. What does E-E-A-T (Expertise, Authoritativeness, Trustworthiness) mean for KYC?
- E-E-A-T is a Google quality standard, but the principle applies perfectly to finance. Your KYC process must be Trusted by regulators and users, Authoritative in its compliance with global standards (like FATF), and demonstrate Expertise in fraud prevention. A strong IDaaS platform is a way to “embed” E-E-A-T into your onboarding process.
13. What is UBO (Ultimate Beneficial Owner) verification?
- This is a critical part of KYC for business accounts (KYB). It’s the process of identifying the real people who own or control a company, even if they are hidden behind layers of shell companies. Advanced IDaaS platforms can help automate this complex research.
14. How does mobile number intelligence stop fraud?
- It analyzes the mobile number itself for risk. For example, has the number been active for years or was it just created? Has it recently been involved in a SIM swap attack? This “metadata” provides powerful, invisible-to-the-user security signals.
15. What is the future of digital identity?
- The future is decentralized, user-centric, and portable. We’re moving toward a single digital identity for all financial services, where users control their own verifiable credentials in a secure digital wallet, giving them seamless, secure access to the global digital economy.